Running the ARTIC nanopore bioinformatics pipeline using EPI2ME
ARTIC pipelines | bioinformatics
| Document: | ARTIC-MPXV-bioinformatics-EPI2ME-SOP-v1.0 |
| Creation Date: | 2024-08-22 |
| Author: | Lauren Lansdowne |
| Licence: | Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License |
artic-mpxv-nf workflow implements an ARTIC FieldBioinformatics pipeline for the purpose of preparing consensus sequences from MPXV genomes that have been DNA sequenced using a pooled tiling amplicon strategy.
This document walks-through how to install and run the ARTIC bioinformatics pipeline in the ONT EPI2ME desktop software.Credits / Acknowledgements
This pipeline is possible due to the ongoing efforts of many people developing and maintaining bioinformatics software. For a complete list of acknowledgments please see the documentation on the pipeline Github repository: https://github.com/artic-network/artic-mpxv-nf
Using the ARTIC MPXV analysis pipeline in EPI2ME
Requirements:
- A working installation of EPI2ME. For instructions for installing EPI2ME, see this document.
- Internet access to download the pipeline, and for the first time running it. After that, you should be able to run it offline.
- Details about how the data was generated including the primer scheme used and the base-caller specified within the MinKNOW software.
Import the workflow
- Open EPI2ME. On the main dashboard select “View workflows”:
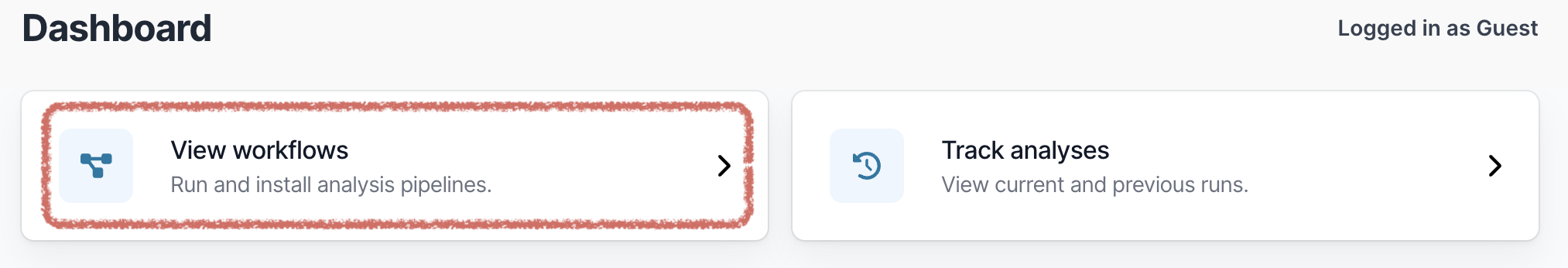
- Then select “Import workflow”:
-
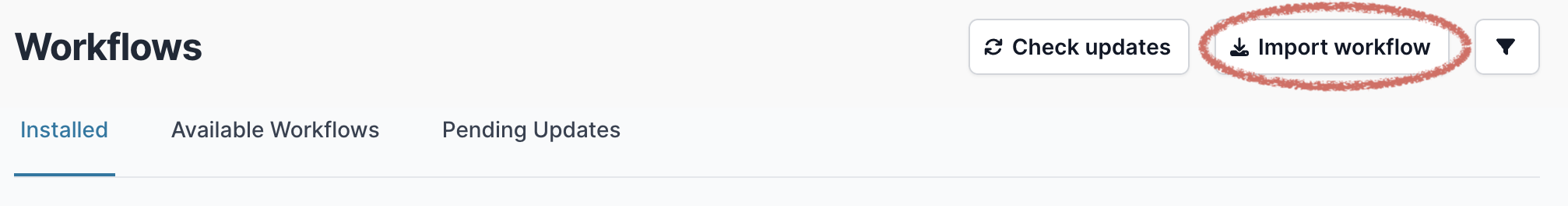
- A pop-up window will appear where you can enter the GitHub URL. Enter the URL (
https://github.com/artic-network/artic-mpxv-nf) and click “Download”: -
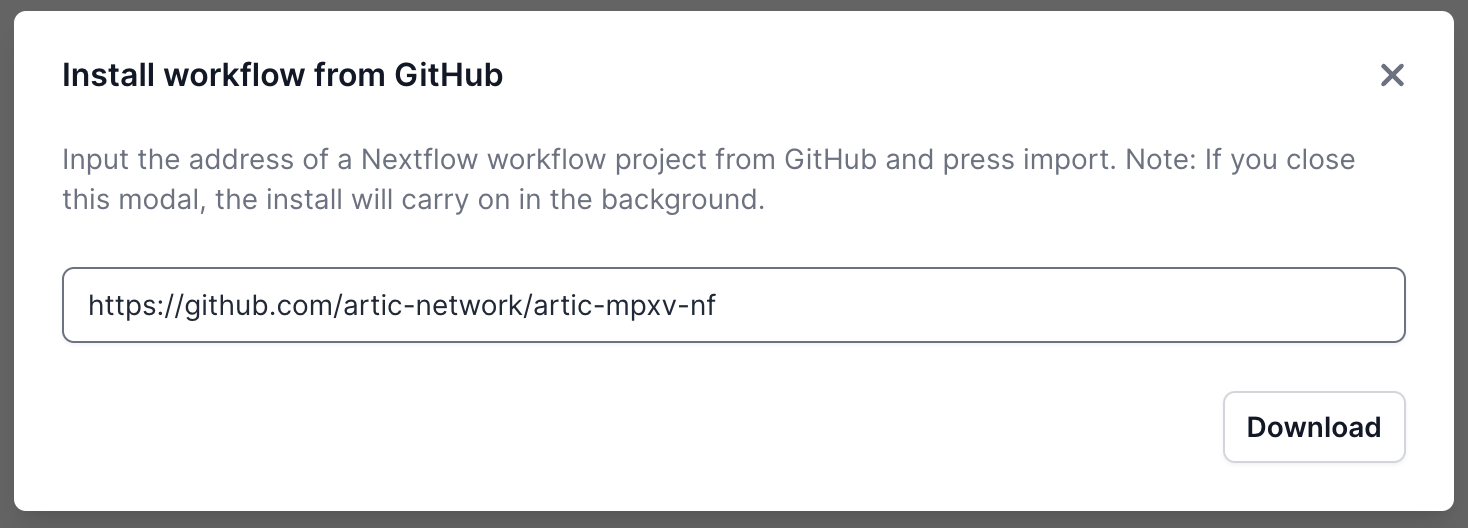
Once it has downloaded, it will be ready in the Installed tab:
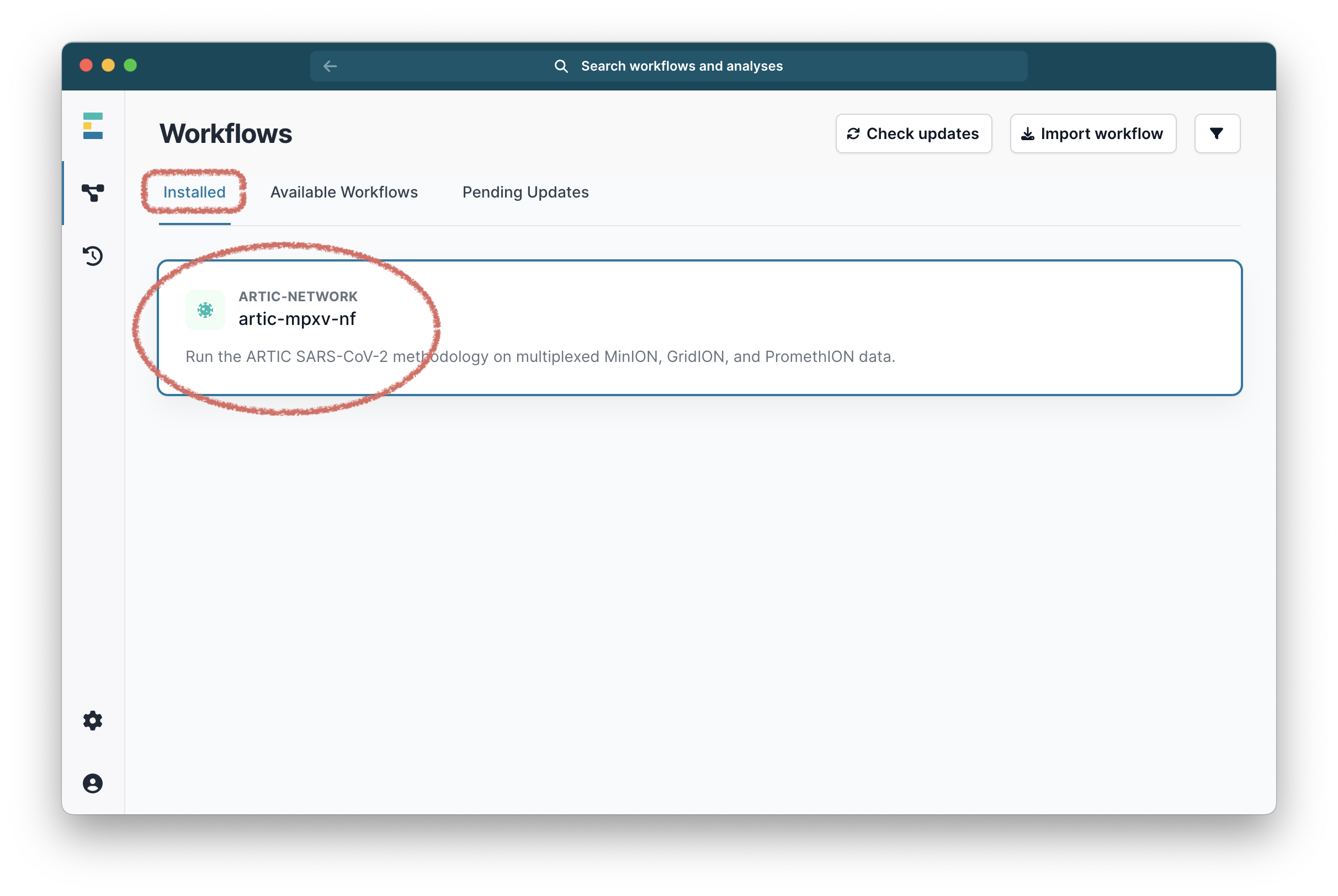
Select it and you will be taken to a landing page for this workflow.
Running the workflow
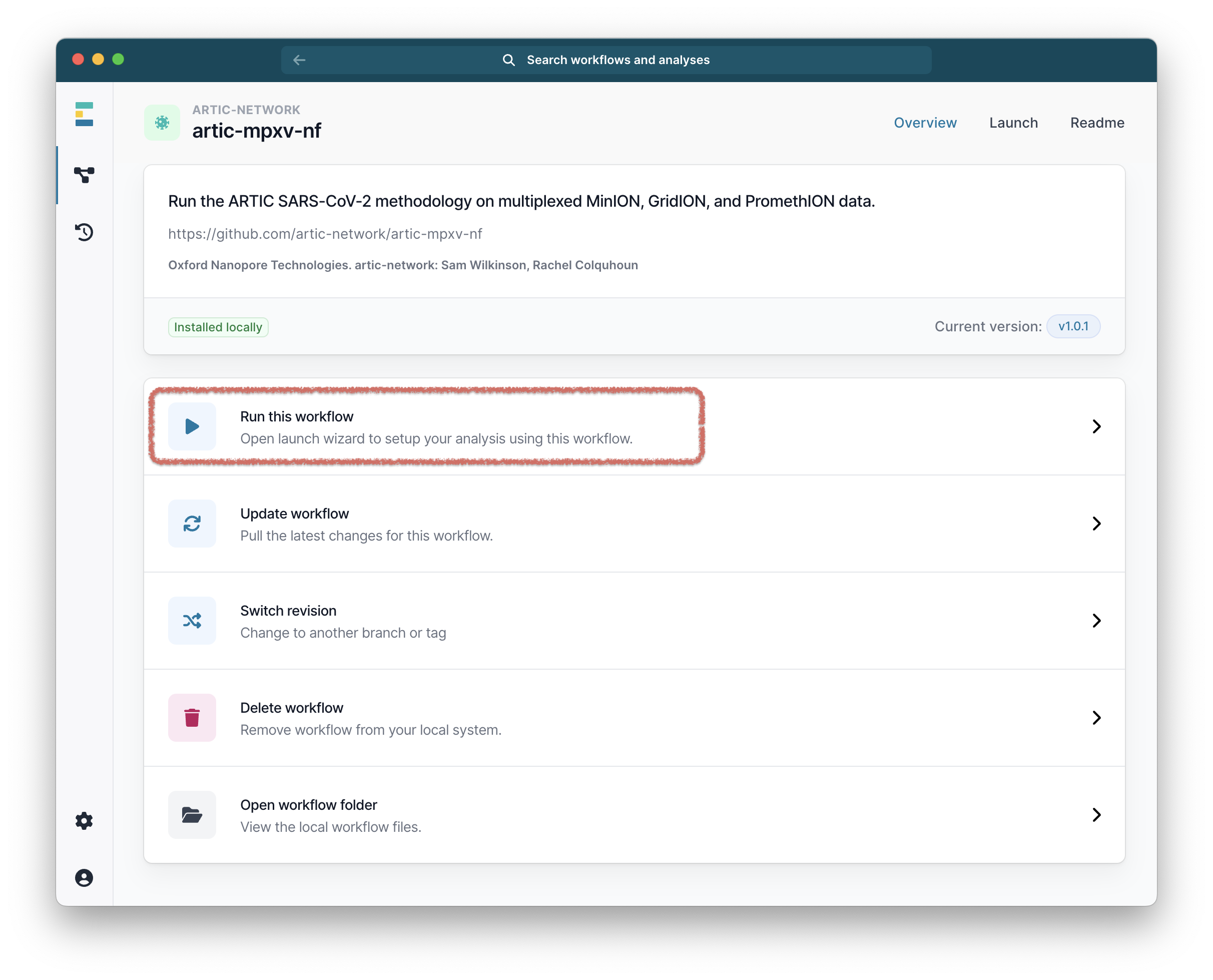
From the workflow landing page, click “Run this workflow”.
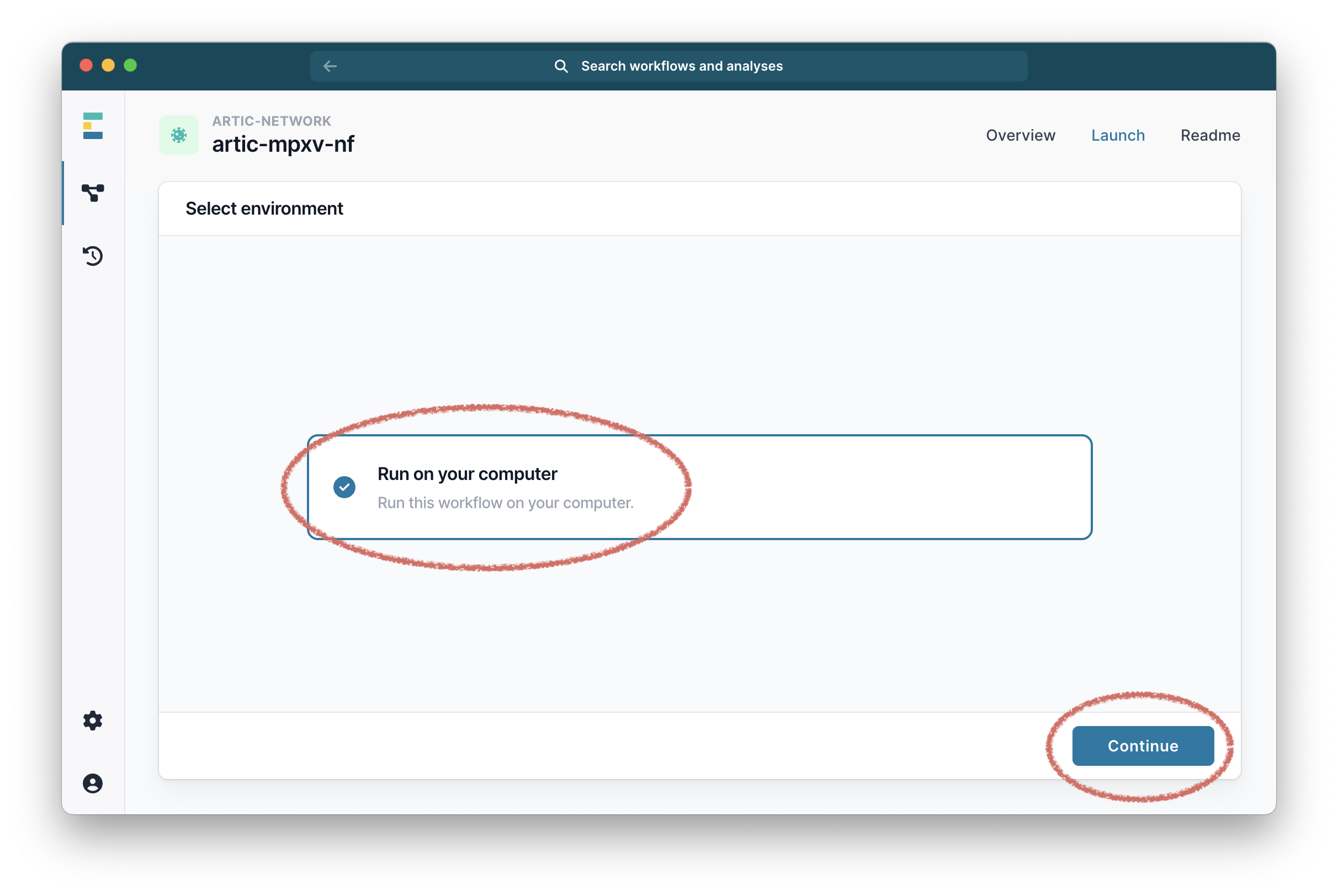
Then select “Run on your computer” and click “Continue”.
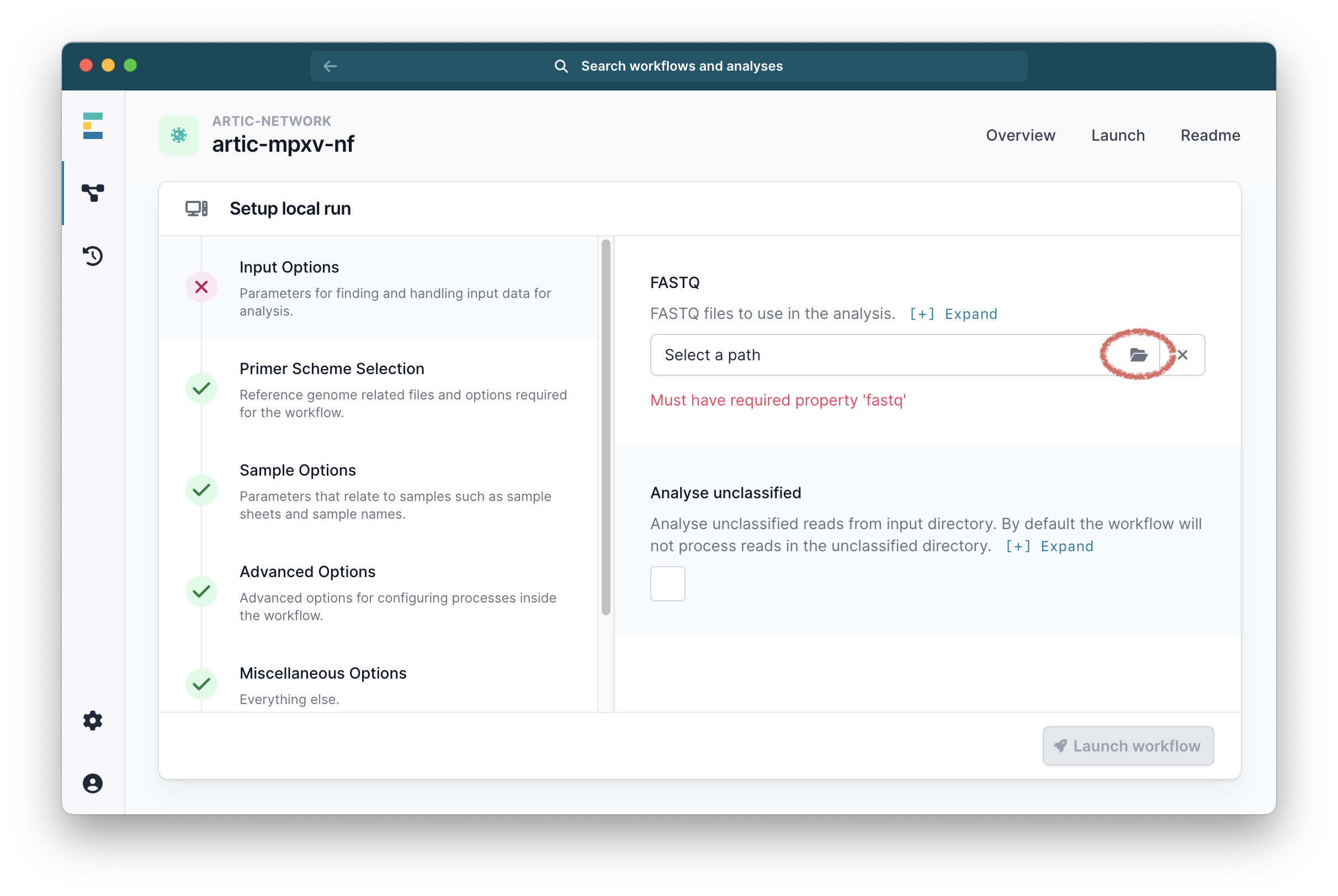
At this point EPI2ME will show you a panel called “Setup local run” which will give you all the options and settings for the workflow.
The first settings are the “Input Options” where it will ask you to select your FASTQ folders. This will usually be the fastq_pass folder in the base-called output of MinKnow. Click the folder icon to select the folder you want:
Next go to the “Primer Scheme Selection” tab and make sure that the primer scheme matches the one you used:
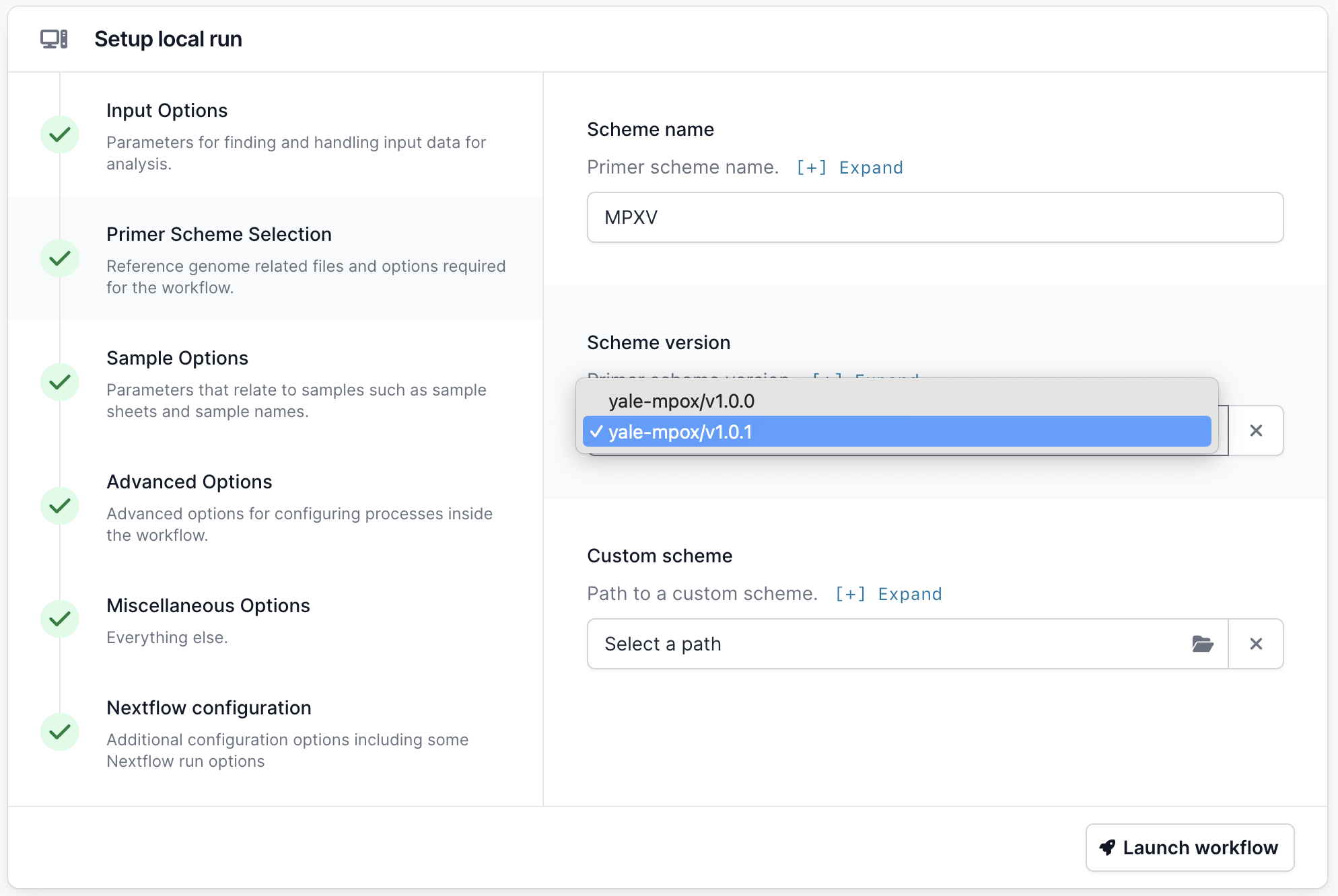
If your scheme is not listed, you can use the “Custom scheme” section to provide the full path to the directory containing your appropriately named scheme bed and fasta files — <SCHEME_NAME>.bed and <SCHEME_NAME>.fasta.
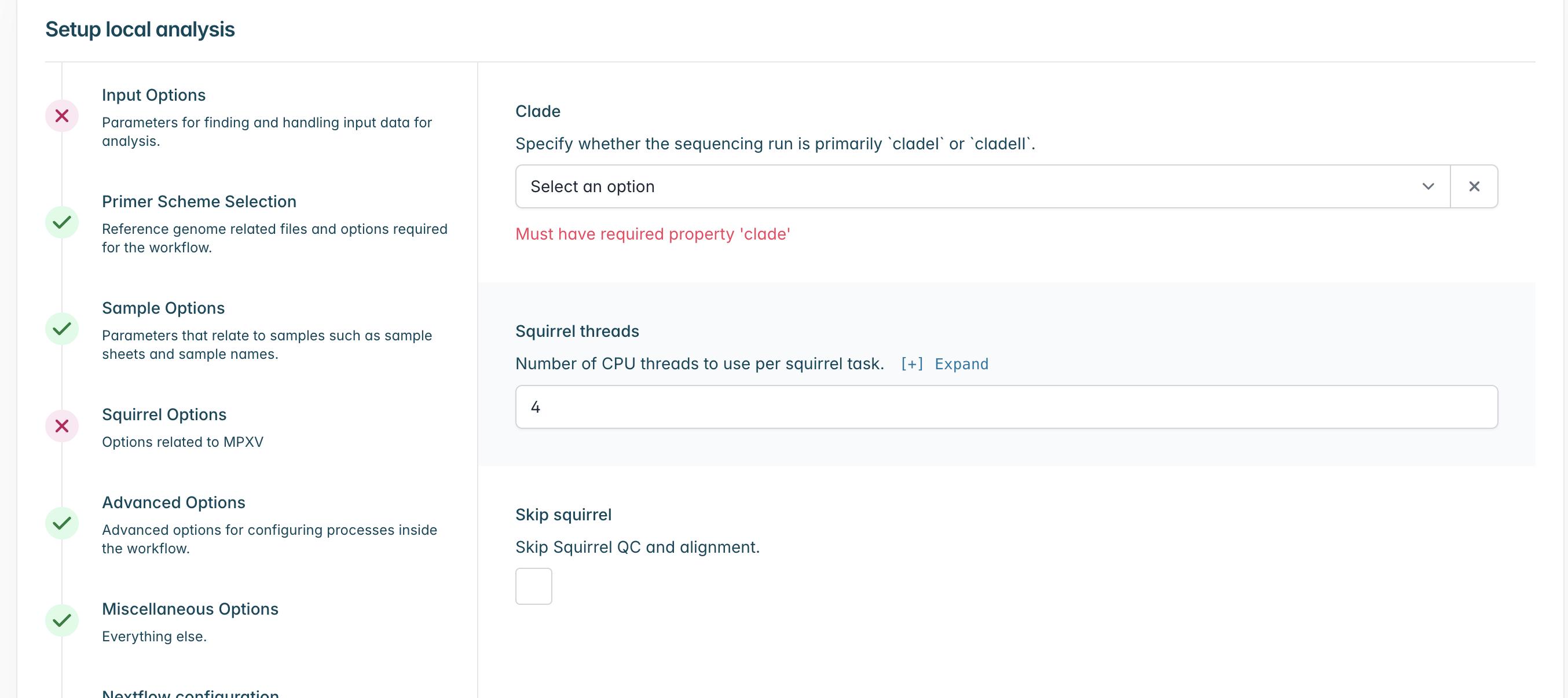
Go to “Squirrel Options” and select the clade which your sequences most likely belong to, if you are unsure of the specific subclade or you have a mixture within your sequencing run you may select a higher level clade (e.g. cladei). If you do not wish to run squirrel you may also select “Skip Squirrel” to skip it.
Next go to the “Sample Options” tab to provide details about the samples (and controls) that match each barcode:
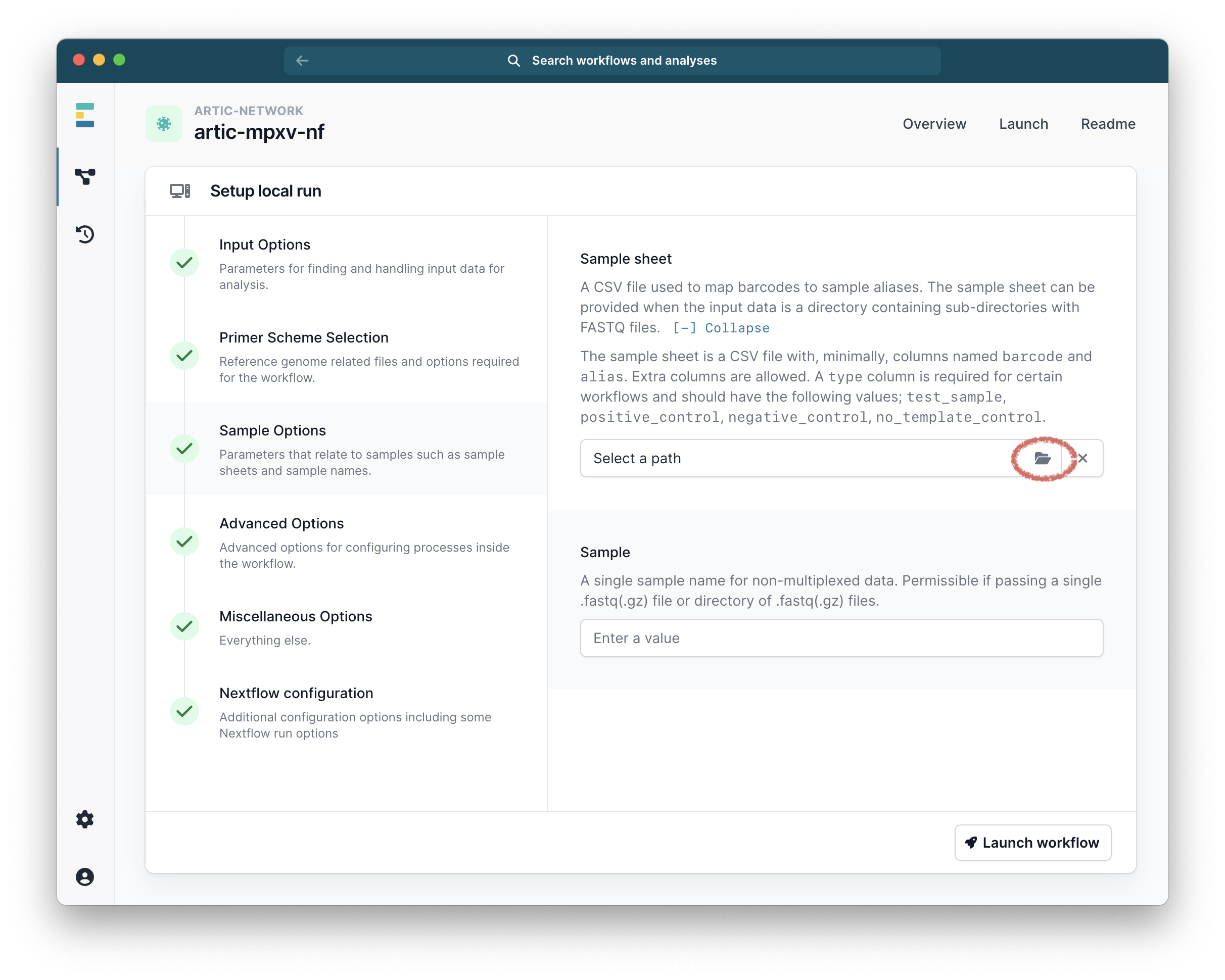
Samples Sheet This is a CSV file that maps the name of each barcode in the run to a sample ID that will be used to name the output consensus sequences.
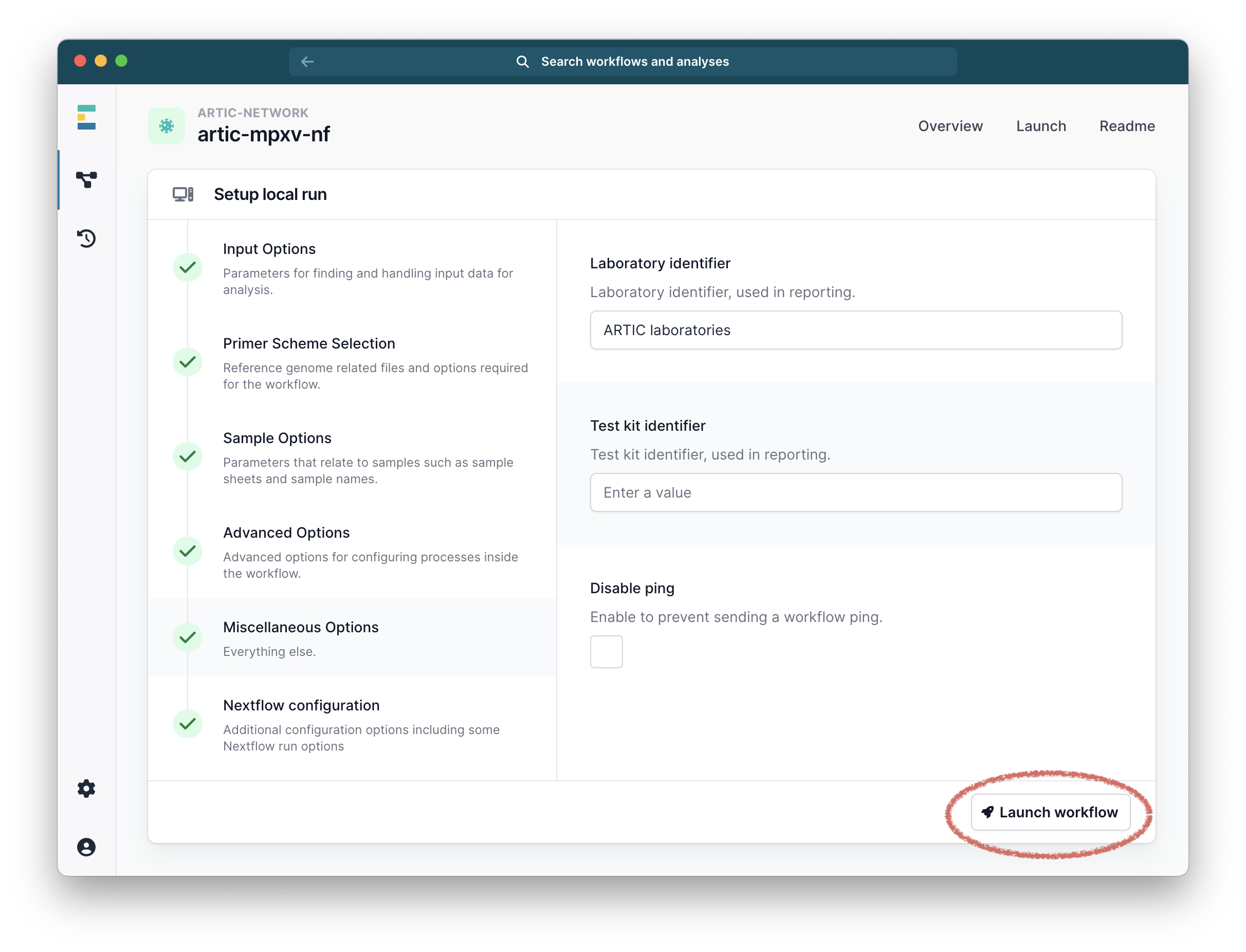
Finally, click “Launch Workflow” and then “Launch”:
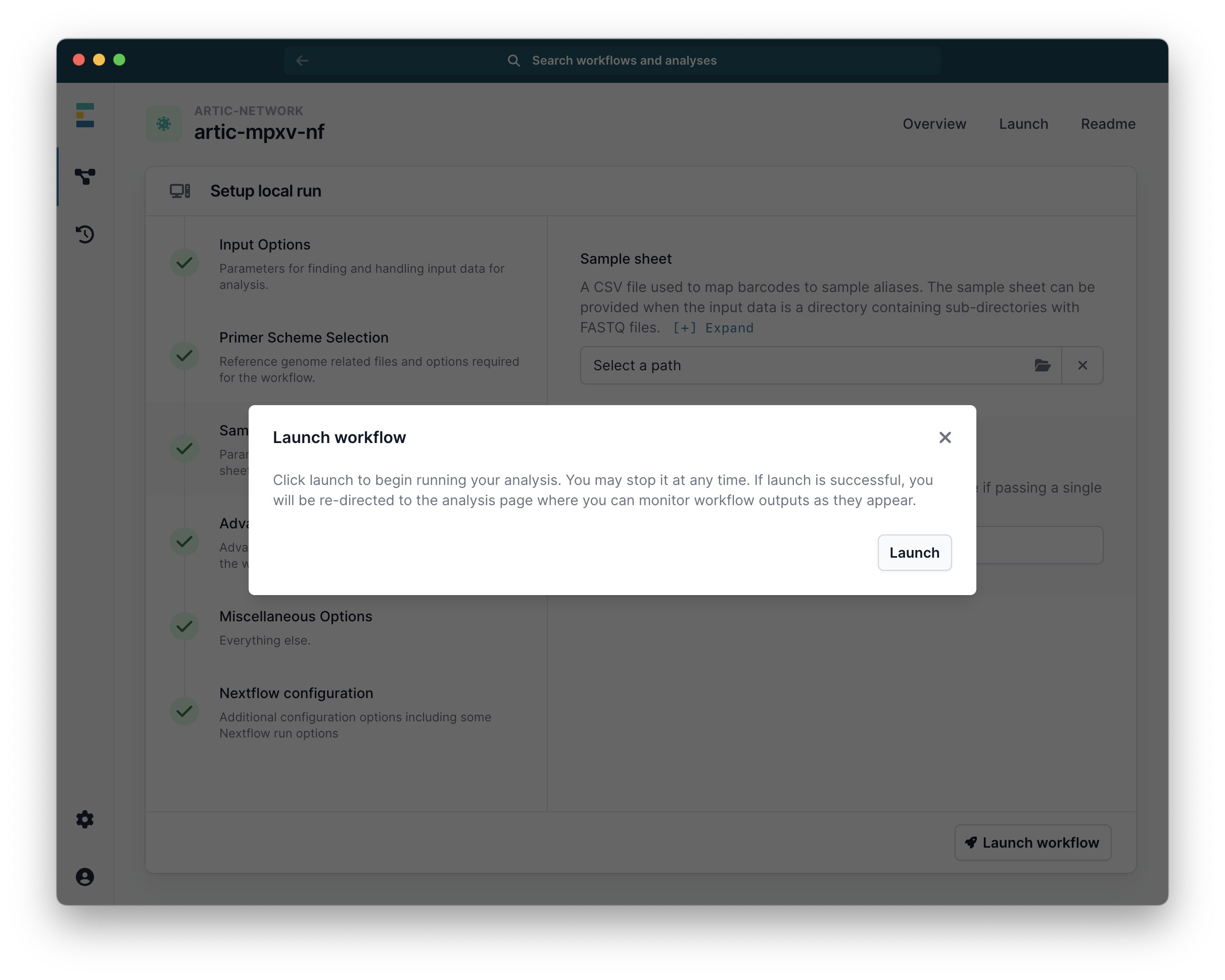
The pipeline will then start running. The run-time will depend on the size of your files, the number of barcodes and the speed of your computer, but a few minutes per barcode is common. While it is running you will see a series of progress bars, and at the top a blue ‘Running’ icon. This will change to green and ‘Complete’ when it has finished.
When it has finished you will have a collection of outputs for both consensus and individual barcodes.
Advanced Options
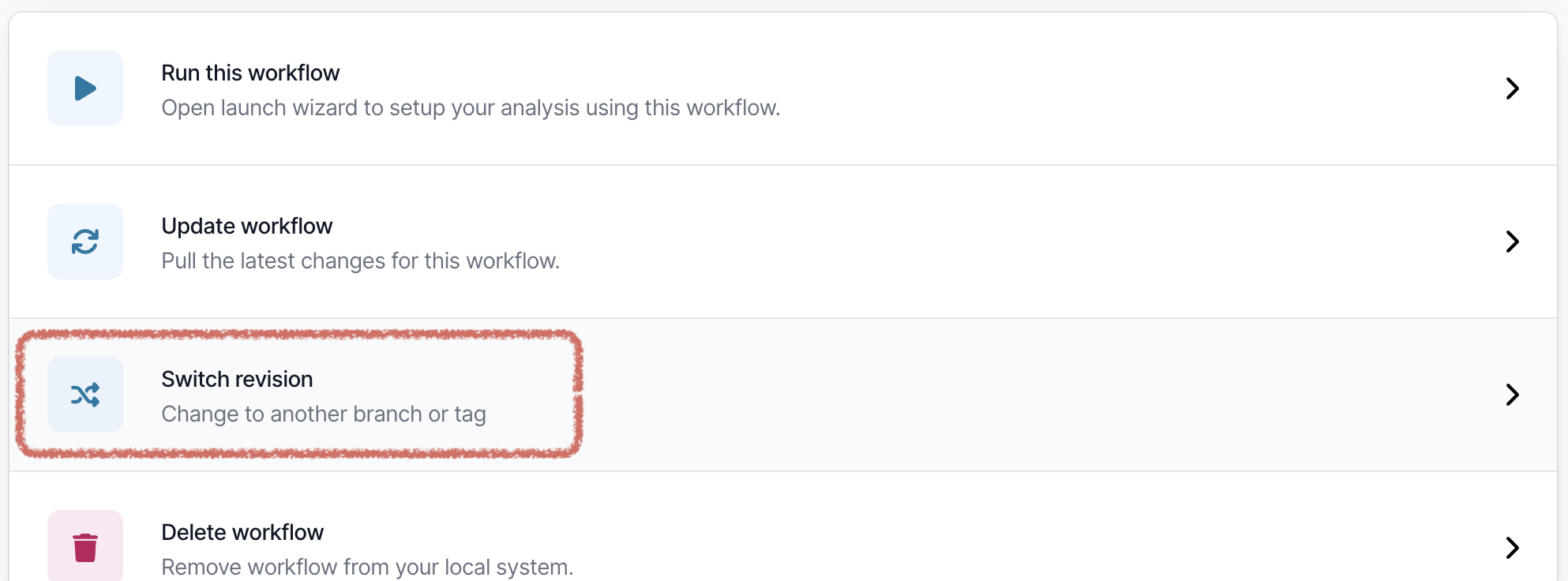
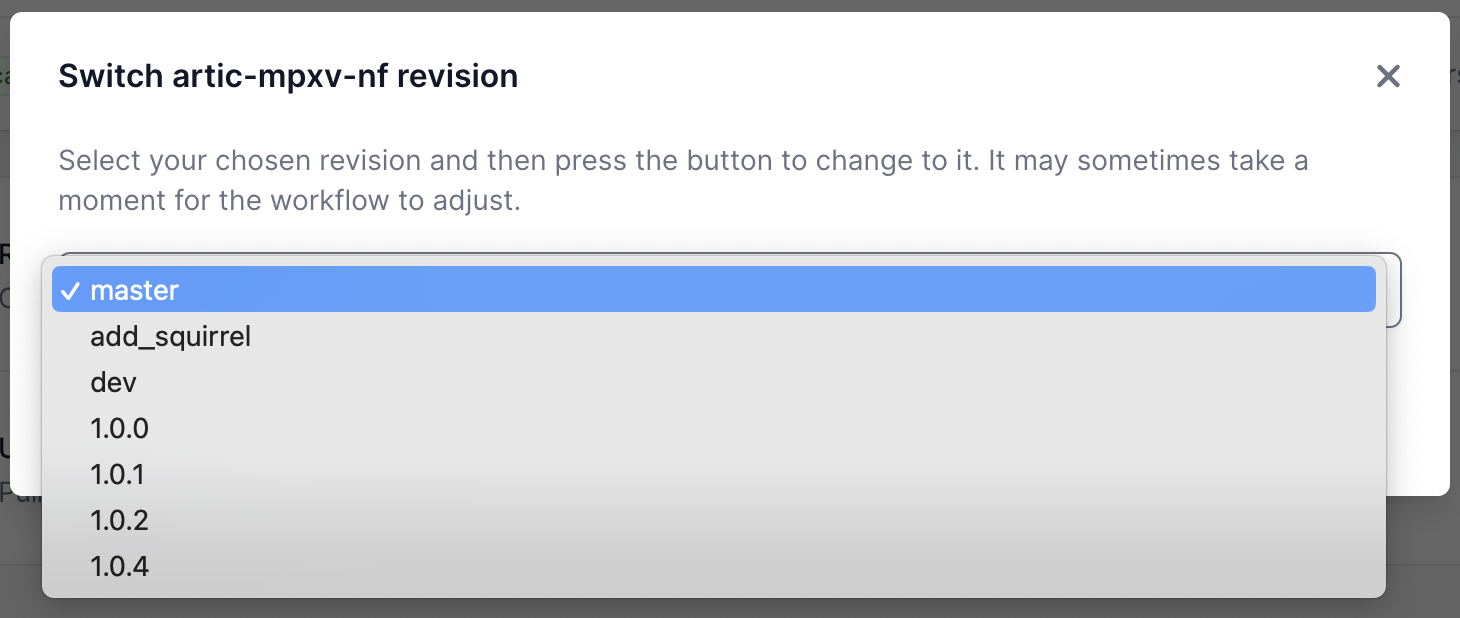
Changing the pipeline version
If you need to use a previous or a development version of the pipeline, this can be selected from the workflow landing page.
Overriding the basecaller configuration for variant caller model selection
Medaka runs within the pipeline to call variants between the reads provided and the reference. It will try to auto-select a variant calling model based upon the “basecall_model_version_id” field within the FASTQ read header. If it is unable to auto-select (for example if your data was basecalled with a version of MinKNOW which is no longer supported) you may need to choose an option from this drop down list of available models in “Advance Options” (scroll down).
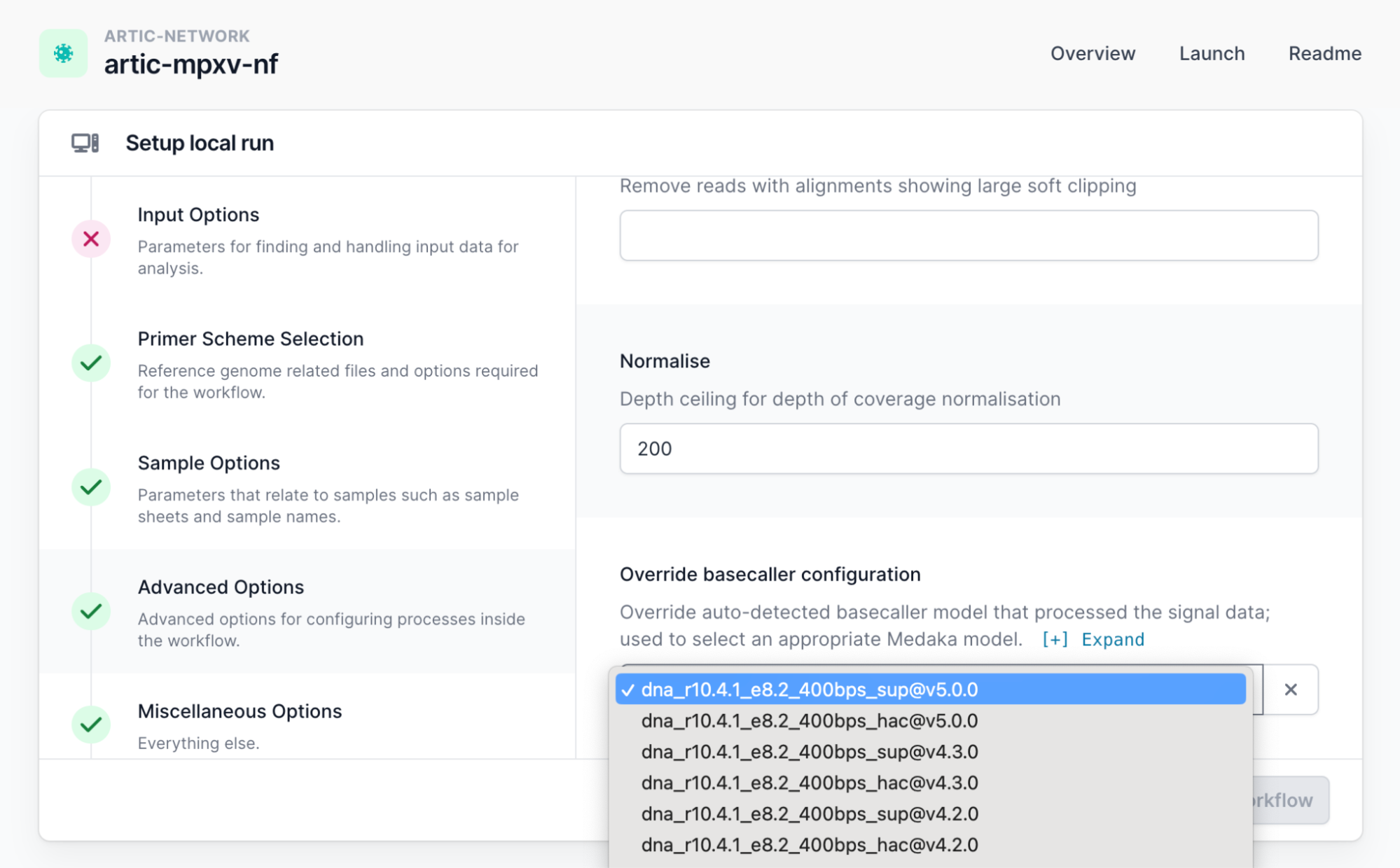
We recommend you use a supported version of MinKNOW. As a work around, you should select an option from this list of models which matches the flowcell chemistry and sequencing speed at a minimum for medaka to function normally. For example, if you have used an r9.4.1 flowcell on run at 450bps translocation speed (standard) you will need to select the “dna_r9.4.1_450bps_hac” basecaller configuration so that the pipeline can select an appropriate medaka model.
Related documents:
This pipeline can also be run in a command-line environment. See this document for detailed instructions for doing this.